Ghana’s Cocoa Export Revenue Hits Lowest Levels Since 2018
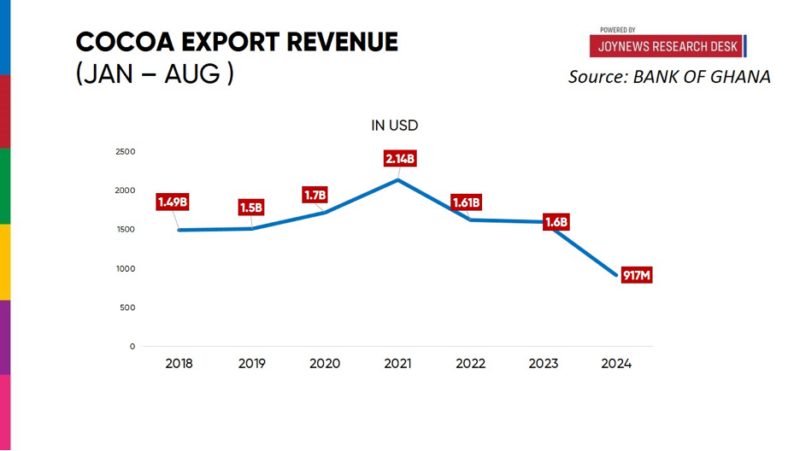
Data from the Bank of Ghana’s latest Summary of Economic and Financial Data reveal a worrying drop in export revenues, with cocoa earnings between January and August 2024 falling to $917 million, the lowest since 2018.
This marks a sharp shortfall from the $1.6 billion earned during the same period last year—a $683 million gap that could severely impact the government’s efforts to stabilize the cedi.
The decline extends a downward trend that has plagued the cocoa sector since its peak in 2021, when Ghana’s cocoa exports reached $2.1 billion. Revenues have dropped steadily, falling to $1.61 billion in 2022 and $1.6 billion in 2023.
This year’s plunge marks the first time in six years that earnings have slipped below the billion-dollar threshold.
Ghana’s COCOBOD has also announced plans to gradually phase out reliance on the Cocoa Syndicated Loan, which has traditionally been a vital financial cushion for the sector.
However, given the loan’s importance in stabilizing both the cedi and the broader economy, the Bank of Ghana is exploring alternative measures.
During a recent Monetary Policy Committee meeting, Governor Dr. Ernest Addison revealed that the central bank is now shifting focus to its Gold Purchase Program as a contingency plan in light of uncertainties surrounding the future of the syndicated loan.
“We are aware that COCOBOD is more or less replacing the syndicated loan, but we think that we have enough reserves from our gold exports as insurance in case things don’t go as expected on the cocoa side,” Dr. Addison said.
Source: Caleb Wuninti Ziblim




